Mastering the COSO Enterprise Risk Framework: A Comprehensive Guide
The COSO Enterprise Risk Framework (COSO ERM) is essential for managing business risks and enhancing corporate governance. Initially developed to prevent financial fraud, it helps organizations establish robust internal controls and integrate risk management into their strategic planning. This article will guide you through the key components of COSO ERM, its evolution, and practical steps for implementation.
Key Takeaways
- The COSO ERM Framework is essential for public companies, establishing strong internal controls to combat fraudulent activities and integrate risk management with strategic goals.
- The framework consists of five key components—Control Environment, Risk Assessment, Control Activities, Information and Communication, and Monitoring Activities—each crucial for effective risk management.
- Implementing the COSO Framework involves assessing current practices, prioritizing components based on organizational needs, and ensuring continuous improvement for sustained effectiveness.
Understanding the COSO Enterprise Risk Framework
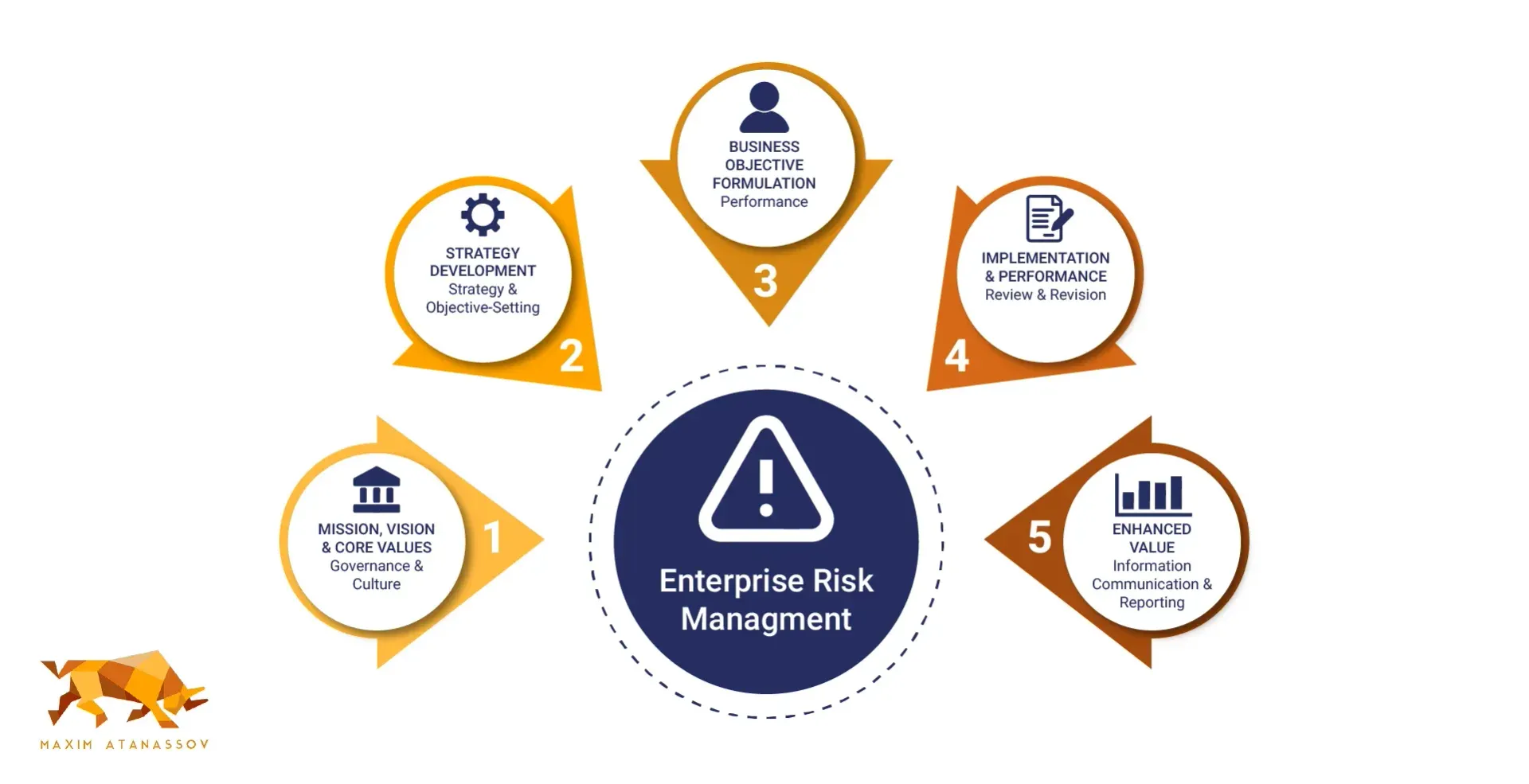
The COSO Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Framework serves public companies by establishing robust internal controls to combat fraudulent financial reporting. Developed to enhance corporate governance following major financial scandals, the framework has significantly influenced risk management practices across various organizations. Released in 2004, the COSO ERM Framework aimed to establish a foundation for effective risk management while adapting to modern challenges like cybersecurity.
Over the years, the COSO framework has undergone significant updates to remain relevant in an evolving business environment. The 2017 update, for instance, linked enterprise risk management with strategy and performance, emphasizing the integration of risk considerations into strategic planning. This connection ensures proactive risk management practices that align with an organization’s mission and long-term goals.
The structure of the COSO ERM Framework facilitates continuous improvement in risk management practices, making it applicable to organizations of all sizes. Embedding the framework into their operations allows organizations to establish a strong risk culture, enhance risk awareness, and maintain effective internal control systems.
Key Components of the COSO Framework
The COSO Framework is built on five core components that work synergistically to enhance internal control effectiveness. These five components are:
- Control Environment
- Risk Assessment
- Control Activities
- Information and Communication
- Monitoring Activities
Each component plays a vital role in establishing a comprehensive risk management framework, ensuring that risks are identified, assessed, and managed effectively.
We will now explore each of these components in detail.
Control Environment
The control environment sets the ethical foundation and values for an organization, significantly influencing its approach to risk management. It encompasses the core values and ethical standards that govern the organization, laying the groundwork for effective internal controls. A robust control environment ensures that leadership emphasizes the importance of risk management and ethical behaviour, promoting a culture of integrity and accountability.
One of the key elements of the control environment is the segregation of duties, which helps reduce the risk of fraudulent actions and enhances error detection. Communicating effectively with staff embeds risk awareness within the organization, strengthening the internal environment.
Fostering an environment where ethical values and internal controls are paramount enables organizations to manage risks and achieve their strategic objectives.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is a critical component of the COSO framework, involving the identification and analysis of risks to inform risk management strategies. In this process, organizations assess inherent risks—those naturally occurring within the business—and residual risks, which remain after risk responses are implemented. Using both qualitative and quantitative methodologies, organizations can identify risks and gain a comprehensive understanding of their risk landscape.
The framework outlines four main responses to risk: reduce, accept, transfer, or avoid. This structured approach enables organizations to develop targeted strategies to manage different types of risks effectively. The COSO risk assessment model has faced criticism for potentially oversimplifying risk management by focusing too much on internal factors and neglecting external threats.
To counter these criticisms, organizations should consider a range of possible outcomes and take a portfolio view of risk. This comprehensive approach ensures that adverse consequences of both one-off events and gradual trends are monitored, aligning assessed risks with the organization’s risk tolerance and risk appetite. By doing so, organizations can make informed decisions that support their strategic goals.
Control Activities
Control activities consist of specific policies and procedures implemented to mitigate risks effectively. These activities ensure that risk responses are executed as intended, encompassing a mix of prevention and detection controls. A sound internal control system integrates both manual and automated controls, providing a balanced approach to managing risk.
These activities can include everything from authorization and approval processes to reconciliations and verifications. By embedding these control activities within their business processes, organizations can ensure that their risk management strategies are robust and capable of addressing various risk scenarios.
Information and Communication
Effective information systems are crucial for the timely communication of risk-related data, aiding decision-making processes. In the digital age, the ability to quickly disseminate information across an organization can significantly enhance risk management efforts. Timely risk communication fosters risk awareness among stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is informed and prepared to respond to potential risks.
Establishing clear channels for reporting and sharing information ensures that relevant data reaches the right people at the right time. This proactive approach to information and communication supports effective risk management and enhances overall organizational governance.
Monitoring Activities
Ongoing monitoring ensures that risk management practices remain effective and continuously improved. This involves regular reviews and assessments of the control environment, control activities, industry practices, and risk responses to identify any areas that need enhancement.
The internal audit function plays a pivotal role in this process, providing independent evaluations of the effectiveness of risk management practices. Continuously monitoring and adapting their risk management strategies helps organizations remain resilient in the face of evolving risks and challenges.
Evolution of the COSO ERM Framework
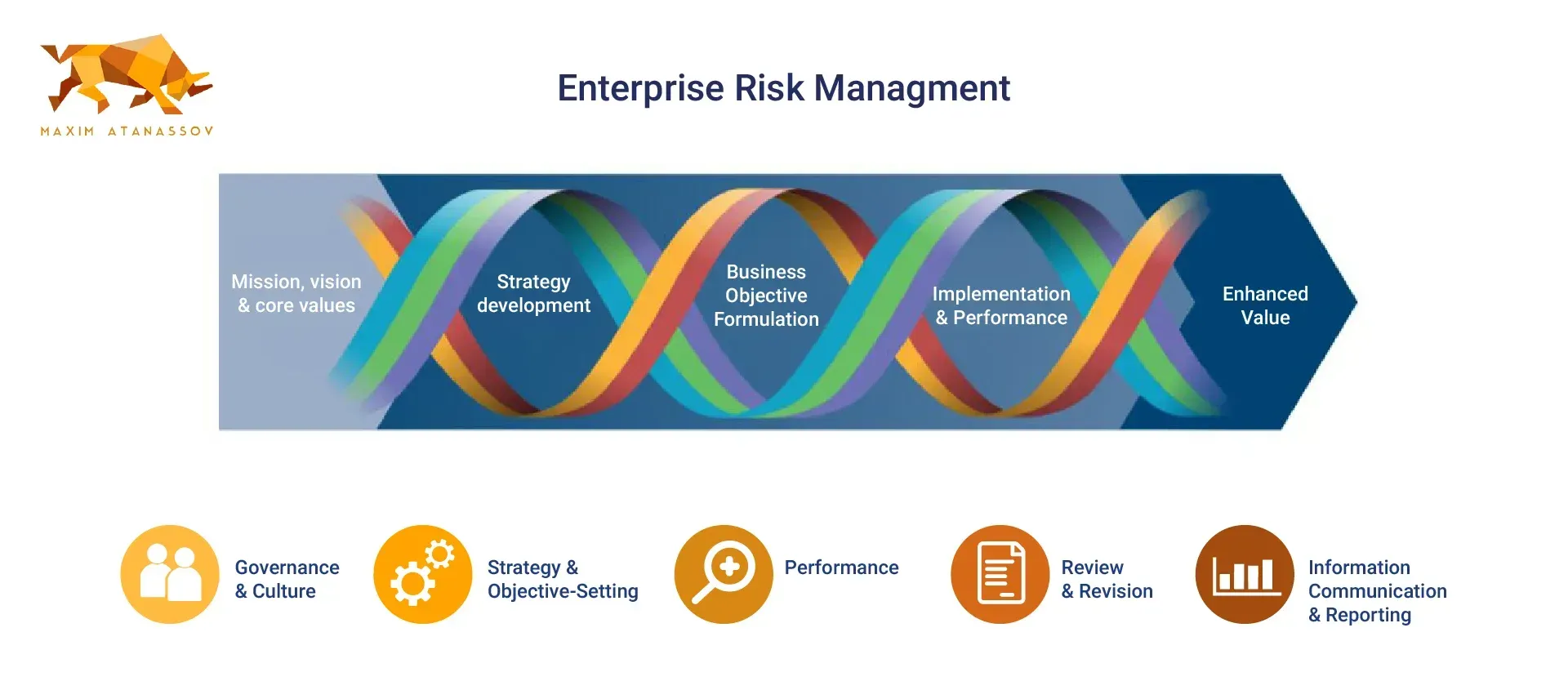
Introduced in 1992, the COSO framework helps organizations assess their internal control systems. Since then, it has evolved significantly, with major updates in 2013 and 2017 to address the complexities of modern business environments. The 2013 update introduced 17 internal control principles and ‘The COSO Cube,’ offering a comprehensive visualization of risk management processes.
The 2017 revision marked a significant shift by emphasizing the integration of risk management with strategic planning and performance management. This update introduced 20 principles aimed at effectively managing risks associated with strategic and business objectives. Aligning risk considerations with strategy and performance helps organizations navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape.
Emerging technologies in cloud computing and data analytics are recognized as pivotal tools in the updated framework, supporting informed decision-making. Regular updates and improvements to the COSO ERM framework ensure ongoing relevance and effectiveness by adapting to evolving risks and organizational changes.
Integrating Risk Management with Strategy and Performance
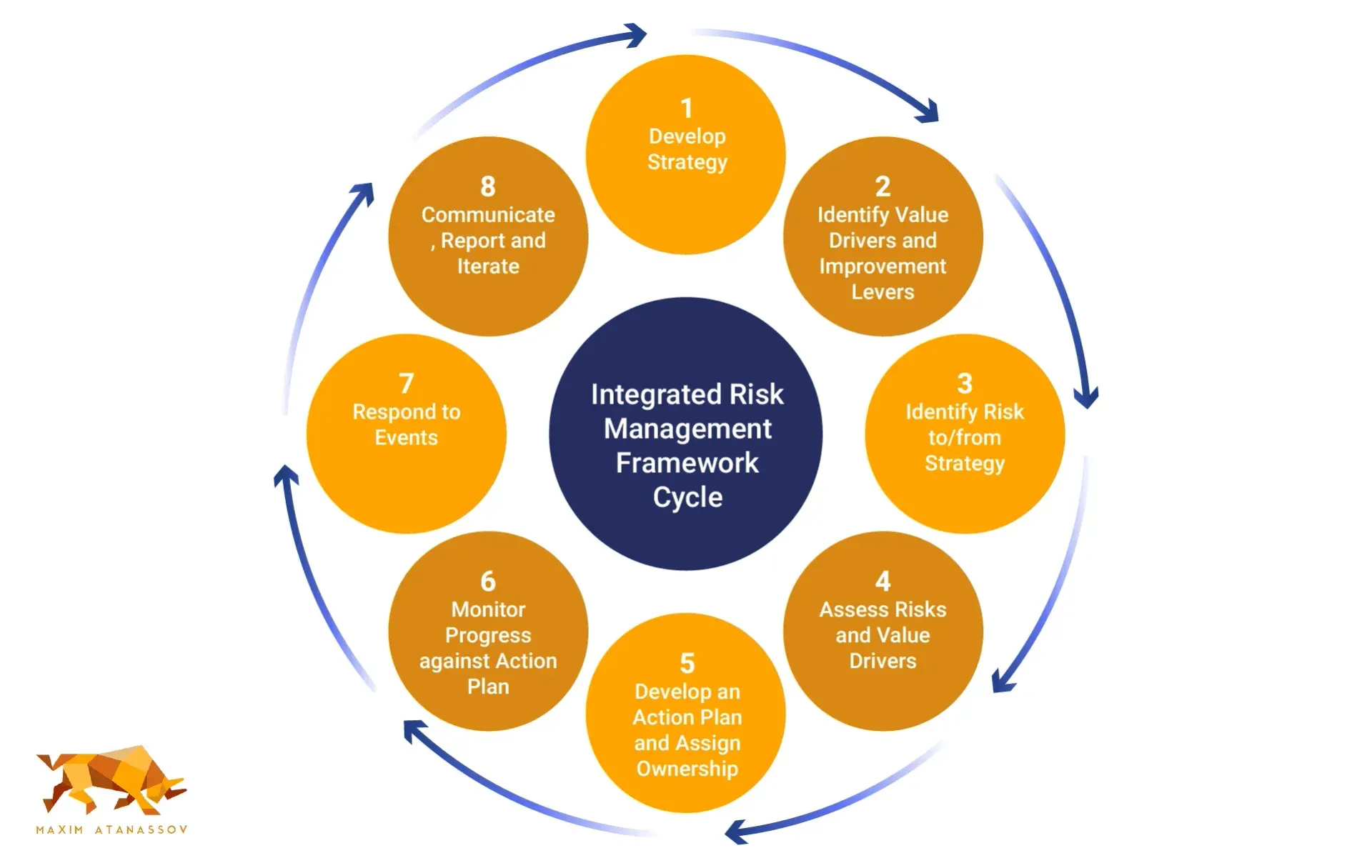
At the core of the updated COSO ERM Framework is the integration of risk management with strategy and performance. Aligning risk management with strategic objectives ensures risk considerations are embedded in all levels of decision-making. This alignment enhances risk awareness and supports the achievement of strategic goals.
Real-world examples illustrate the benefits of this integration. For instance, United Grain Growers utilized a comprehensive data analysis approach to address agricultural risks, integrating their insurance programs for better financial stability. Similarly, Zurich Insurance Group employs Total Risk Profiling to assess and manage risks, ensuring their capital meets regulatory standards while maintaining growth potential.
Embedding risk management into strategy setting and performance management drives performance while effectively managing risks. This holistic approach promotes improved corporate governance and enhanced oversight of business performance.
Implementing the COSO ERM Framework
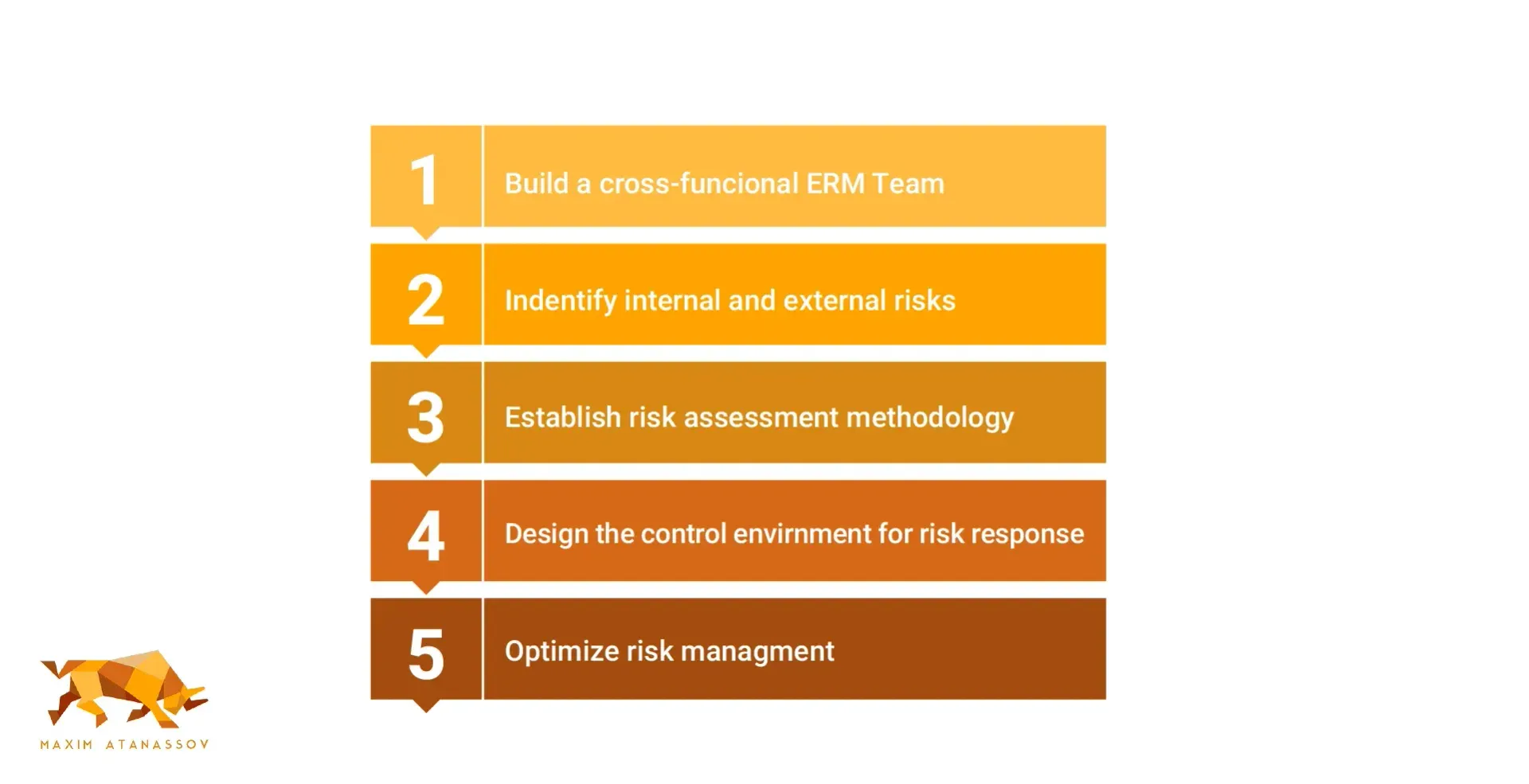
Implementing the COSO ERM Framework requires a phased approach, allowing organizations to manage the integration of components effectively within an integrated framework. Building on successes and identifying areas for improvement ensures a smooth rollout of the framework.
The following subsections will detail the steps involved in assessing current practices, prioritizing components, and ensuring continuous improvement.
Assessing Current Practices
Evaluating current risk management practices is the first step in implementing the COSO framework. Organizations should assess existing practices against the five fundamental principles of the COSO framework to identify gaps and areas for improvement. This evaluation ensures the organization’s risk management strategies align with the framework’s core principles.
Internal auditors play a vital role in this process, providing an independent assessment of the effectiveness of current risk management practices. Their insights can guide the organization in aligning its risk management strategies with the COSO framework, ensuring robust internal controls and effective risk responses.
Prioritizing Components
After assessing current practices, the next step is to prioritize the implementation of the COSO framework’s components based on organizational needs. This involves identifying key areas that require enhancement through surveys, interviews, and internal assessments. Focusing on the most critical components first allows organizations to allocate resources effectively and ensure a targeted approach to risk management.
A tailored implementation plan should outline timelines and responsibilities for each prioritized component. This structured approach allows senior management of the organization to systematically build its risk management framework, addressing the most pressing needs first and building on these successes.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is essential for maintaining effective risk management practices in a changing business environment. Regular updates and monitoring by internal auditors help organizations adapt their strategies to new risks and challenges. This proactive approach keeps the risk management framework relevant and effective over time.
Implementing the COSO framework can streamline organizational processes, resulting in cost savings and increased efficiency. Fostering a culture of continuous improvement enhances organizational resilience and maintains robust internal controls, even as the business landscape changes.
Benefits and Challenges of the COSO Framework

The COSO Framework offers numerous benefits, including uniform business processes, improved efficiency, and effective fraud risk management through structured internal controls. Independent evaluations of risk management practices help organizations identify gaps and areas for improvement, ensuring robust risk management strategies.
However, the framework also presents challenges. Its broad scope and rigid categories can introduce complexity and demand significant resources, potentially hindering its adoption. Despite these challenges, the role of internal auditors is crucial in ensuring compliance and effective implementation of the COSO framework.
Understanding both the benefits and challenges allows organizations to better prepare for the COSO framework implementation, leveraging its advantages while addressing potential hurdles.
Role of Internal Auditors in COSO ERM
As organizations grow in size and complexity, the internal audit function becomes increasingly important. Internal auditors play a critical role in the COSO ERM Framework by providing independent evaluations of risk management practices and ensuring effective internal controls. Their involvement is essential for monitoring and compliance, contributing to robust governance and risk management.
The audit committee and the internal audit department play crucial roles in the evaluation of monitoring. The board sets the company’s tone, which is crucial for ensuring effective governance and compliance. This collaborative approach ensures continuous monitoring and improvement of risk management practices, enhancing organizational resilience.
Case Studies and Examples
Real-world examples demonstrate the practical application of the COSO ERM Framework. Intuit’s ERM program, for instance, has evolved through phases, focusing on ongoing risk assessment and incorporating key risk indicators to enhance strategic decision-making. The University of California redefined its ERM approach by fostering collaboration across departments, leading to substantial cost savings and improved risk management practices.
Statoil employs a unique ERM framework that evaluates both potential downsides and upsides of risks, enhancing value creation while minimizing accidents. Lego has structured its ERM to adapt to various risks through a phased approach, enterprise risk management integrating strategic risk management with operational processes for better resilience.
These case studies showcase the versatility and effectiveness of the COSO ERM Framework in different organizational contexts.
Summary
The COSO Enterprise Risk Management Framework is a powerful tool for organizations seeking to enhance their risk management practices and achieve strategic objectives. By understanding and implementing its key components—control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, and monitoring activities—organizations can establish robust internal controls and effectively manage risks. The evolution of the COSO framework highlights its adaptability to modern business complexities and emerging risks, ensuring its ongoing relevance.
Integrating risk management with strategy and performance is crucial for aligning risk considerations with organizational goals, driving performance, and fostering a risk awareness culture. By adopting a phased approach to implementation, continuously assessing current practices, prioritizing key components, and embracing continuous improvement, organizations can successfully implement the COSO ERM Framework and reap its benefits.
Ultimately, mastering the COSO framework equips organizations to navigate uncertainties, safeguard their values, and achieve long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the COSO Enterprise Risk Management Framework?
The COSO Enterprise Risk Management Framework is a widely recognized standard that guides organizations in establishing effective internal controls and managing risks, thereby enhancing corporate governance. It was initially developed in response to major financial scandals to improve risk management practices.
What are the key components of the COSO Framework?
The key components of the COSO Framework are Control Environment, Risk Assessment, Control Activities, Information and Communication, and Monitoring Activities, all of which function collaboratively to strengthen internal control effectiveness.
How does the COSO framework integrate with an organization's strategy and performance?
The COSO framework seamlessly integrates risk management with an organization's strategy and performance by embedding risk considerations into decision-making processes across all levels. This alignment ensures that a thorough understanding of potential risks informs strategic planning.
What are the benefits of implementing the COSO Framework?
Implementing the COSO Framework leads to uniform business processes and improved efficiency, alongside effective fraud risk management and enhanced oversight of business performance. These benefits result in stronger internal controls, ultimately bolstering organizational resilience.
What role do internal auditors play in the COSO ERM Framework?
Internal auditors play a vital role in the COSO ERM Framework by independently evaluating risk management practices, ensuring effective internal controls, and supporting governance and compliance efforts. Their contributions are essential for monitoring and enhancing risk management strategies.
Share

Maxim Atanassov, CPA-CA
Serial entrepreneur, tech founder, investor with a passion to support founders who are hell-bent on defining the future!
I love business. I love building companies. I co-founded my first company in my 3rd year of university. I have failed and I have succeeded. And it is that collection of lived experiences that helps me navigate the scale up journey.
I have found 6 companies to date that are scaling rapidly. I also run a Venture Studio, a Business Transformation Consultancy and a Family Office.
